Renewable energy sources include wind power, solar power, hydro power, tidal power, geothermal energy, biofuels and the recyclable/reusable part of waste. The use of renewable energy is loaded with benefits, such a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, the diversification of energy supplies and a reduced dependency on fossil fuel markets – in particular, oil and gas. The growth of renewable energy markets is also a potent player in job creation.
For the renewable power producer, the economic logic is straight forward: waste materials or solar energy with neutral or negative impact on business operations (through waste management expenses) can now be harnessed for private energy production.
In short, green energy offers substantial advantages to the climate, health outcomes of people and economic growth.
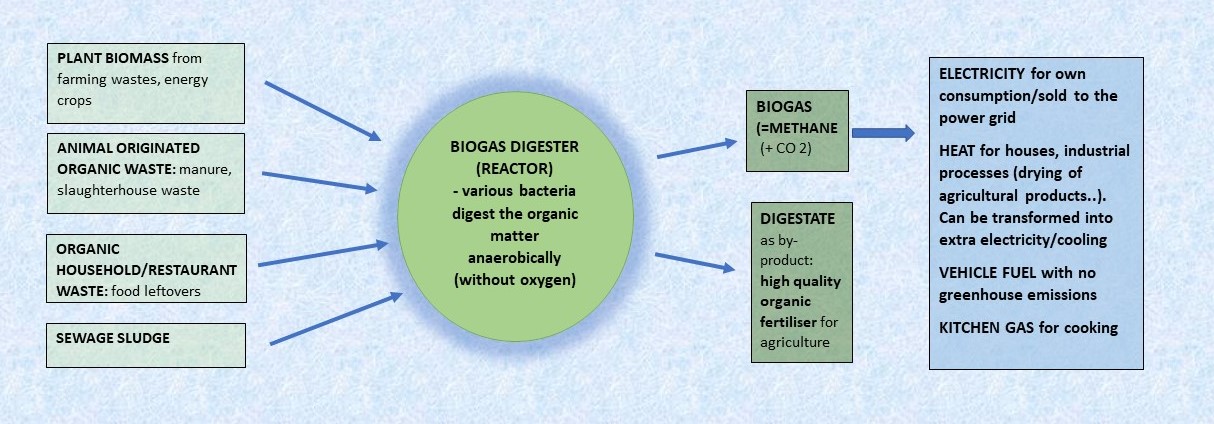
In countries with a restricted electricity infrastructure and erratic power supply, off-grid green energy solutions such as biogas and solar energy power plants are a real game changer. They enable companies and communities to create their own energy in a sustained, non-polluting way. Selling surplus green energy to the power grid often proves economically lucrative, adding clean profit to the producer’s pocket.